
WeatherAsset is a global weather monitoring platform for the fresh produce sector
Access 7-day forecasts, seasonal outlooks and long-term growing location data all in one place
Step 1
You choose your locations
A single location is approximately 10km2
Anywhere in the world
With or without weather stations
A single location is approximately 10km2
Anywhere in the world
With or without weather stations
Step 2
We tailor the weather data
Tell us what impacts your crops
We'll combine the weather variables into custom indicators of growing conditions to provide deeper insight
Tell us what impacts your crops
We'll combine the weather variables into custom indicators of growing conditions to provide deeper insight
Step 3
You get insight for each location
Service is accessible via an intuitive online interface or an API
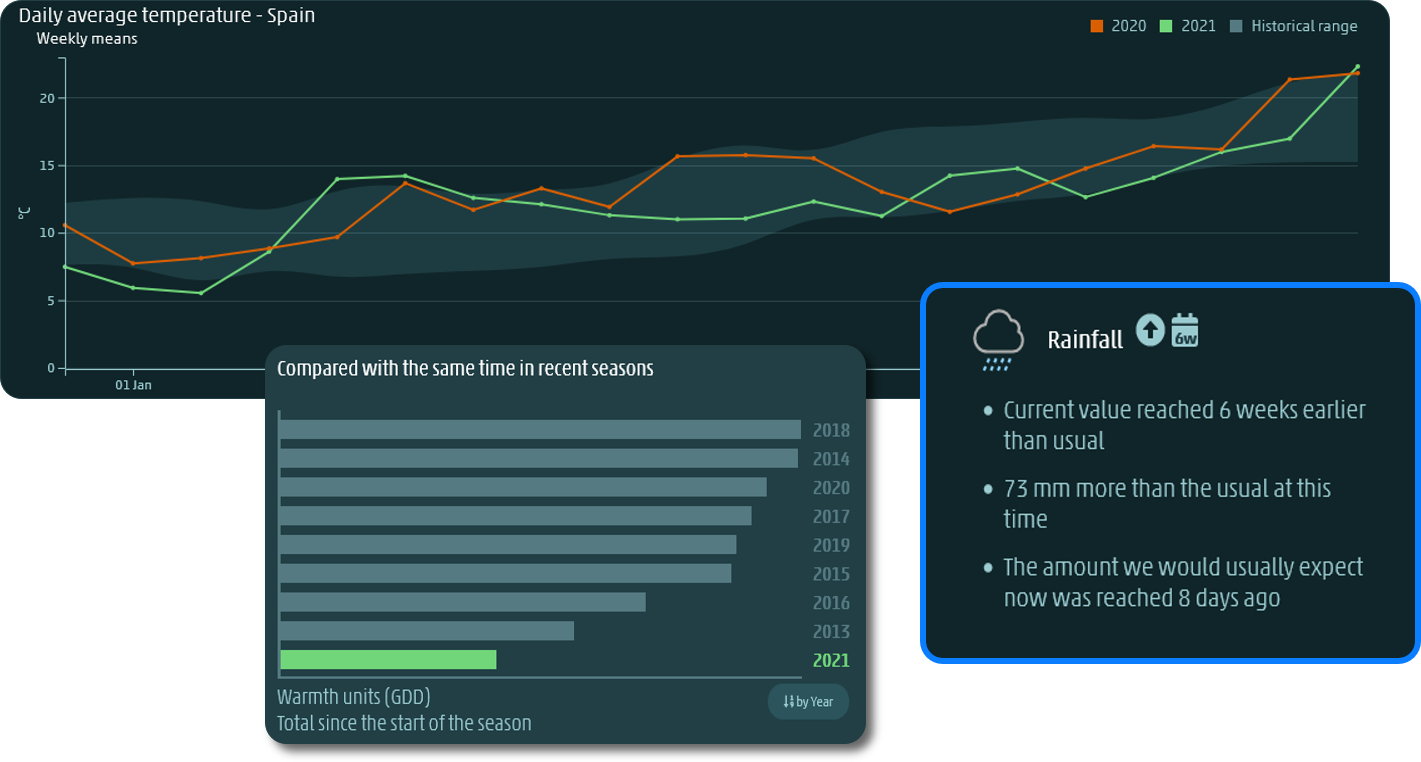
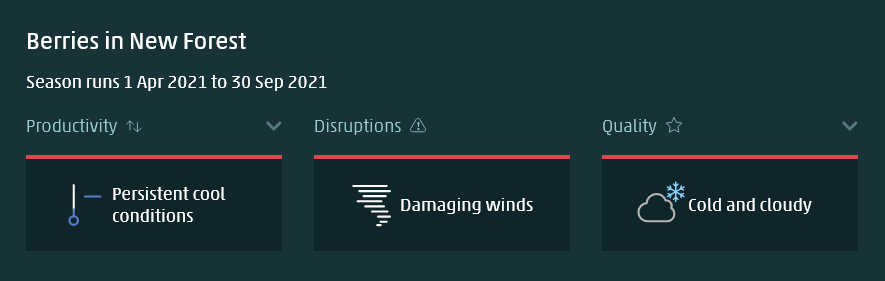
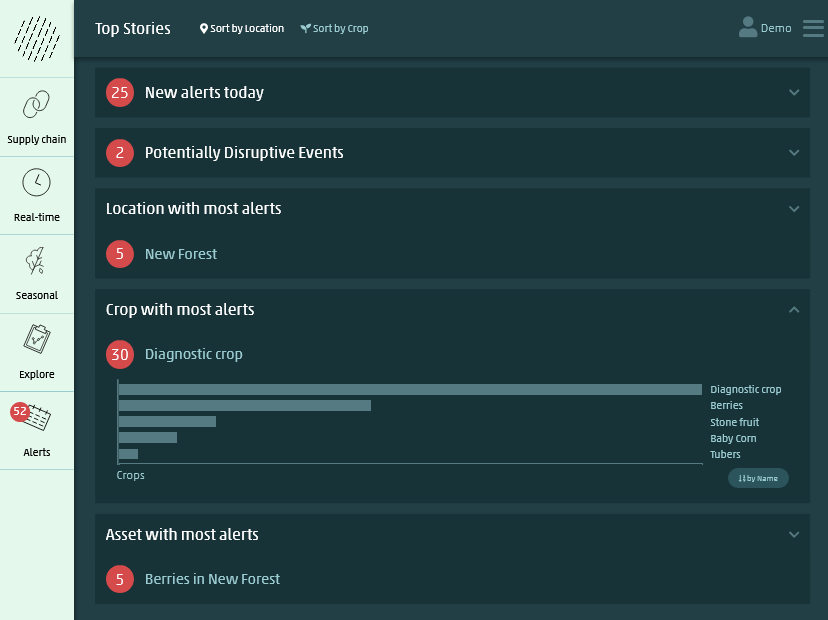
Service is accessible via an intuitive online interface or an API
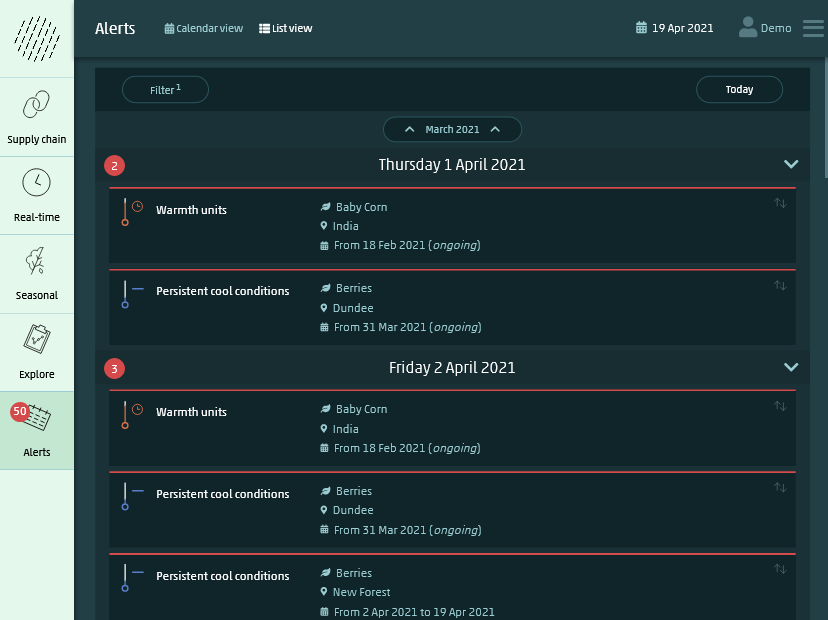
Platform features
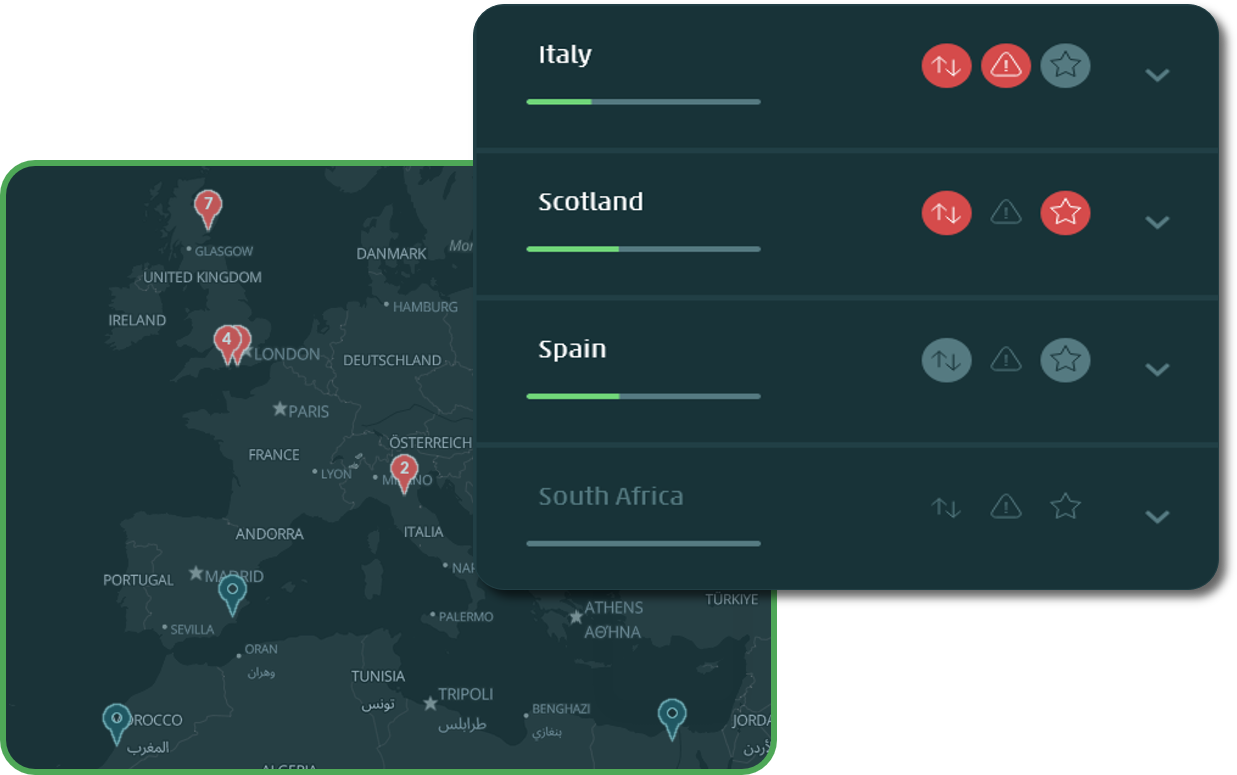
Quick glance summary of prevailing risks for all monitored locations
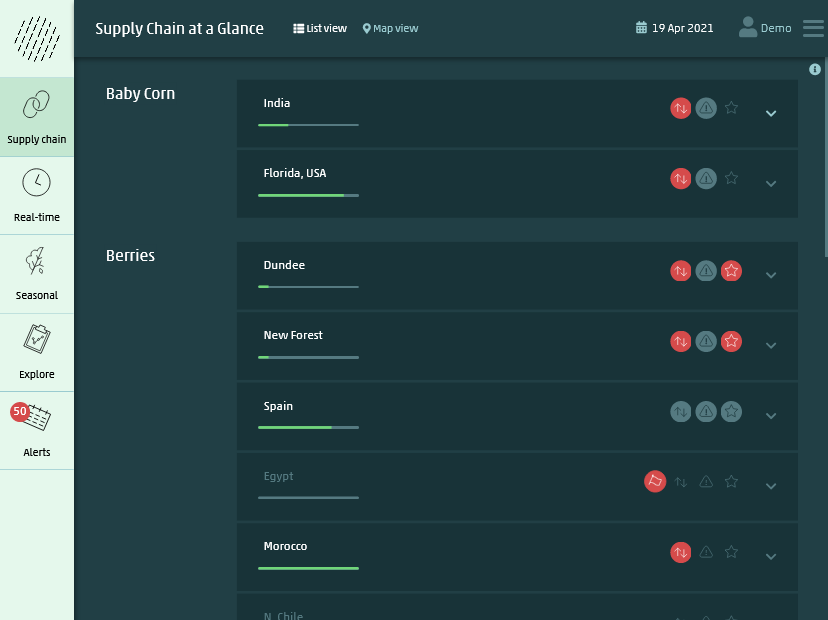
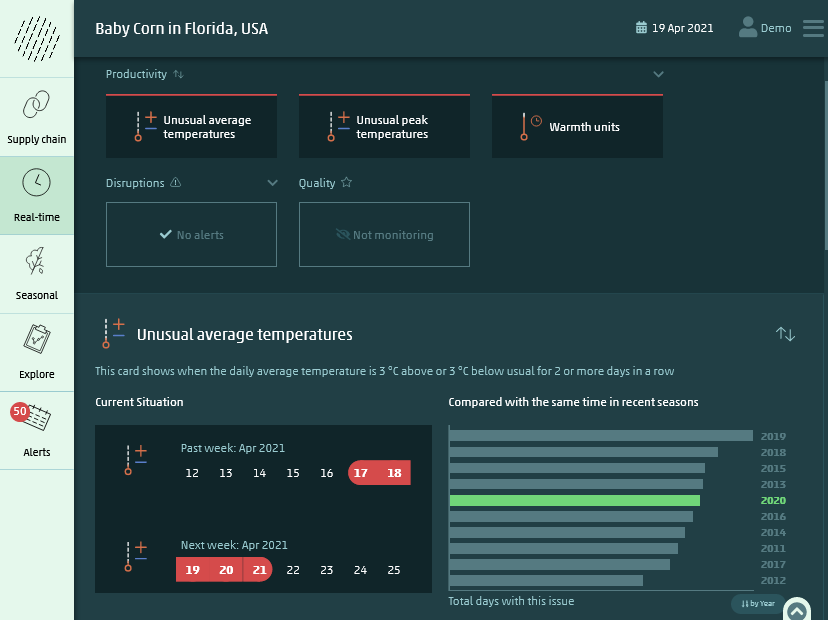
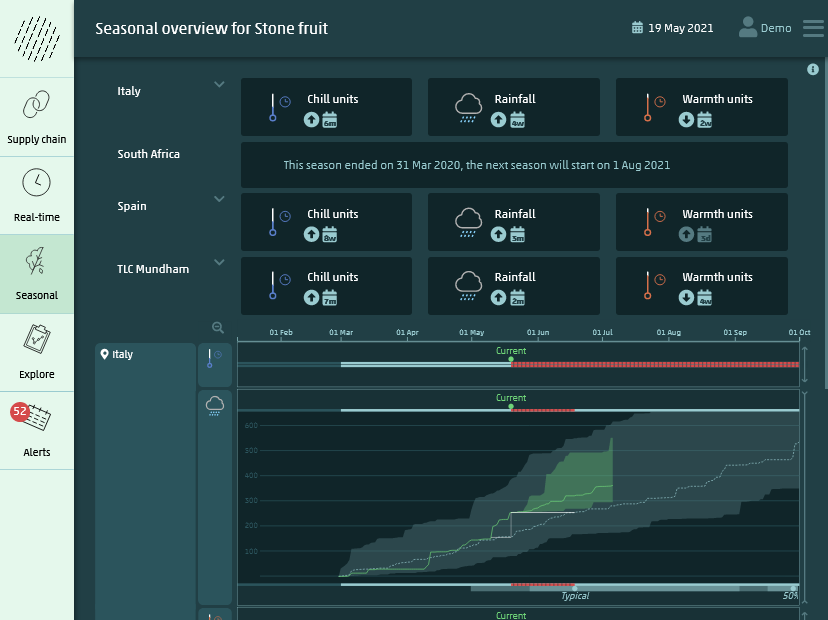
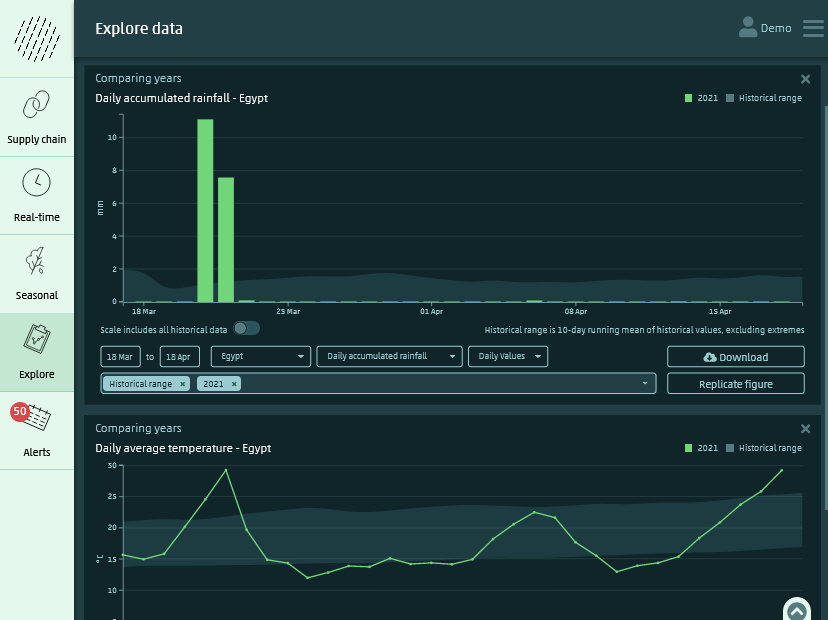
How WeatherAsset is different
Global coverage | |
20+ years of comprehensive weather data | |
Custom indicators of growing conditions tailored to your specific concerns | |
History matching algorithm for more insightful seasonal outlooks |
Ability to ingest your on-site weather station data | |
Create charts and graphs for reports and presentations | |
Alerts and condition summaries direct to your inbox | |
Raw data available via API service |
Global coverage | |
20+ years of comprehensive weather data | |
Custom indicators of growing conditions tailored to your specific concerns | |
History matching algorithm for more insightful seasonal outlooks | |
Ability to ingest your on-site weather station data | |
Create charts and graphs for reports and presentations | |
Alerts and condition summaries direct to your inbox | |
Raw data available via API service |
Pricing is per location at competitive monthly rates
How we do it
No black boxes, just the information you need, all ready to go
What others have to say
WeatherAsset has become a key tool for the Barfoots team to gain insight into the weather across our global supply base. Climate change and extreme weather events are creating frequent challenges and WeatherAsset helps us track these events.
Continuity of supply requires an understanding of what has happened and what is likely to happen in the future and this system helps us do just that.
Technical Director, Barfoots UK
We are using the WeatherAsset API to access historical and predicted weather data to support our satellite analytics service.
It is very easy to use and integrate with our data services platform, and provides a highly useful source of weather data.
Principal Consultant, Environment Systems Ltd
Keeping track of growing conditions across multiple crops and crop varieties throughout our global supply chain is critical, but tricky, particularly as we see increasing climate change-related variabilities. WeatherAsset is a new tool for Worldwide Fruit which has rapidly become key for us to better manage weather-related risk throughout our operations.
We started with a set of trial locations and were very pleased with initial results. We are now scaling to a wider set of crops and growing locations and have seen value to business scale as we've increased the roll-out. WeatherAsset is now an important management tool which is particularly helpful in identifying areas that require priority management focus.
Senior Technical Manager, Worldwide Fruit
The team behind WeatherAsset
WeatherAsset comes from the Institute for Environmental Analytics, a world-leading data analytics R&D institute located in Europe’s largest centre for weather and climate research.
Our entrepreneurial team is composed of PhD-educated data scientists, software developers and UX design/visualisation experts with backgrounds in the fields of physics, maths, statistics, climate science and engineering. Together we share a common passion for the environment and a deep understanding of how to turn scientific data into meaningful information for end users.
From understanding climate models to harnessing satellite imagery to assess environmental change, we are experts at turning complex scientific data into actionable information.
As well as WeatherAsset, the IEA offers a range of consultancy services focused around the modelling and analysis of environmental data. Use the buttons below to go to our website or to contact us for more information.
Glossary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Artificial intelligence (AI) | Computer systems able to perform tasks normally requiring human intelligence, such as decision-making. |
Big data | Extremely large data sets are analysed computationally to reveal patterns, trends and associations. |
Climate | The weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period. |
Consultancy, Consulting | Professional expert advice on in the fields of data, weather, environment and more. |
Crop damage, Crop risk | Harm (or potential for harm) that impairs the quality or quantity of plants or plant products that are grown and harvested. |
Data analysis | The extraction of useful information from data to assist decision-making. |
Data science | Combines domain expertise, programming skills, and knowledge of mathematics and statistics to extract meaningful insights from data by looking for patterns in complex datasets to build models that predict what may happen in the future. |
Data visualisation | Any technique for creating images, diagrams or animations to communicate a message. |
Drought | A period of abnormally dry weather long enough to cause a serious hydrological imbalance. Note that drought is a relative term. |
Earth observation | The gathering of information about planet Earth's physical, chemical and biological systems via remote sensing technologies, usually involving satellites carrying imaging devices |
Environmental analysis | Assessment of the predictable long- and short-term environmental effects of a proposed action, and of reasonable alternatives to that action. |
Environmental data | Data collected or produced from measurements, analyses or models of environmental processes. |
Environmental impact | The consequences of realised risks on natural and human systems, where risks result from the interactions of climate-related hazards, exposure and vulnerability. |
Extreme weather | An event that is very rare at a particular place and time of year. This means that a weather event may be considered extreme in one location but not in another, or in one month but not in another. |
Flooding | The overflowing of the normal confines of a stream or other body of water, or the accumulation of water over areas not normally submerged. Floods include river floods, flash floods, urban floods, pluvial floods, sewer floods, coastal floods and glacial lake outburst floods. |
Hail | Pellets of frozen rain which fall in showers. |
Heat stress | Any stress effect on a plant that results from exposure to excessive ambient temperatures or lack of moisture in the soil or atmosphere. |
Heatwave | An extended period of abnormally hot weather. |
Machine learning (ML) | The use of computer systems that are able to learn and adapt without following explicit instructions, by using algorithms and statistical models to analyse and draw inferences from patterns in data. |
Meteorology | The earth science dealing with phenomena of the atmosphere (especially weather). Or a catch-all term encompassing both the weather and the climate of a region. |
Net zero | Net zero emissions are achieved when human-made emissions of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere are balanced by human-made removals over a specified period. |
Rainfall | The quantity of rain falling within a given area in a given time |
Smart Agriculture | The use of technologies like Internet of Things, sensors, location systems, robots and artificial intelligence on farms. |
Storm | A disturbance of the atmosphere marked by wind and usually by rain, snow, hail, sleet, or thunder and lightning |
Weather | The state of the atmosphere at a particular place and time as regards heat, cloudiness, dryness, sunshine, wind, rain, etc. |
Weather analysis, Climate analysis | Detailed examination of the elements or structure of weather/climate. |
Weather analytics, Climate analytics | Information resulting from the systematic analysis of weather/climate data and statistics. |
Weather data, Climate data | Observations of atmospheric conditions of a region which includes indicators such as minimum/maximum temperature, humidity, or wind speed. |
Weather forecasting | Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere, land and ocean and using models to project how the atmosphere will change at any given place over the next few days. |
Weather modelling, Climate modelling | A numerical representation of the weather/climate system based on the physical, chemical and biological properties of its components and their interactions with each other. |
Weather resilience, Climate resilience | The capacity to recover quickly from weather events, frequently by being prepared. |
Weather risk, Climate risk | The potential for adverse consequences where something of value is at stake and where the occurrence and degree of an outcome is uncertain. |



